Welcome to the website of GAC GmbH!
We would like to give you a general picture of the company in the following pages.
News about our market analyses
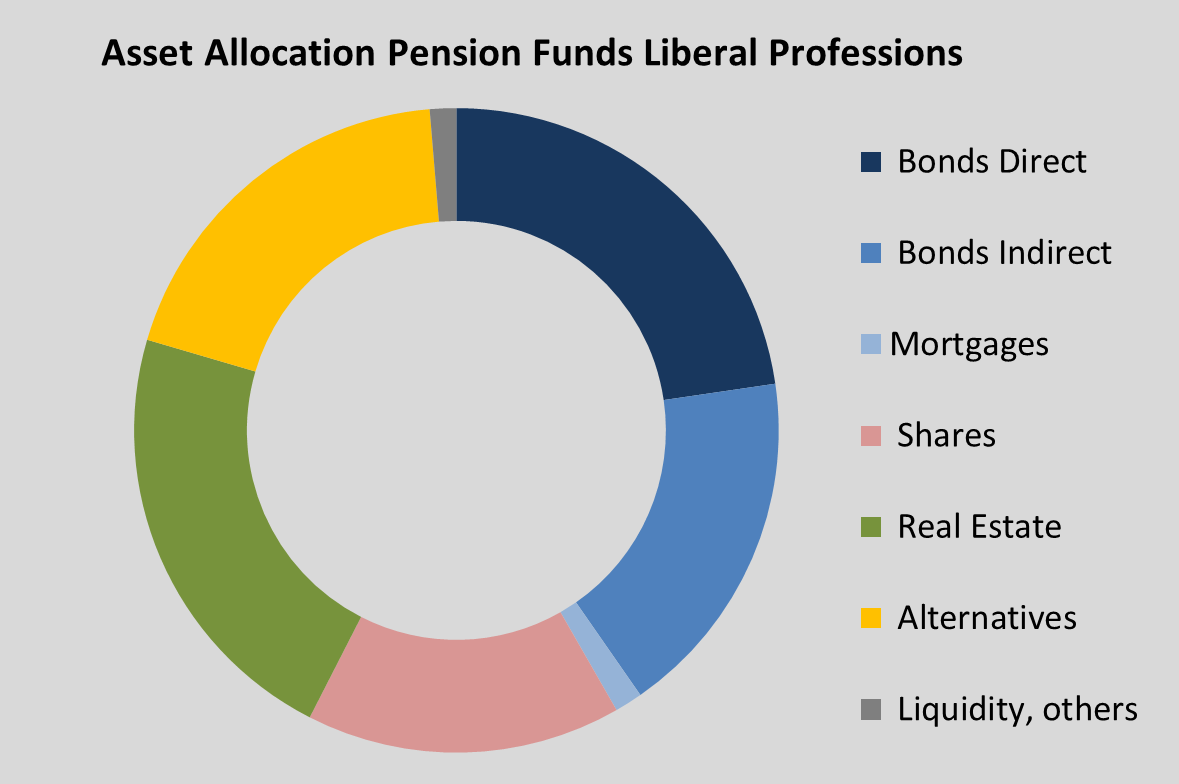
The capital investments of the 92 pension funds for liberal professions continued to grow dynamically in 2024, rising by almost 5% to around €300 billion. Forty-eight institutions manage assets worth billions, 17 of them at least €5 billion. Direct bond investments continued to expand as in the previous year (23%). While the overall proportion of bonds rose slightly to 42%, the proportion of equities fell slightly further to just under 16%. The weighting of real estate in the overall allocation decreased slightly (22%), while alternatives were further expanded (19%). In 2024, pension funds achieved an average net return of around 3.5%.
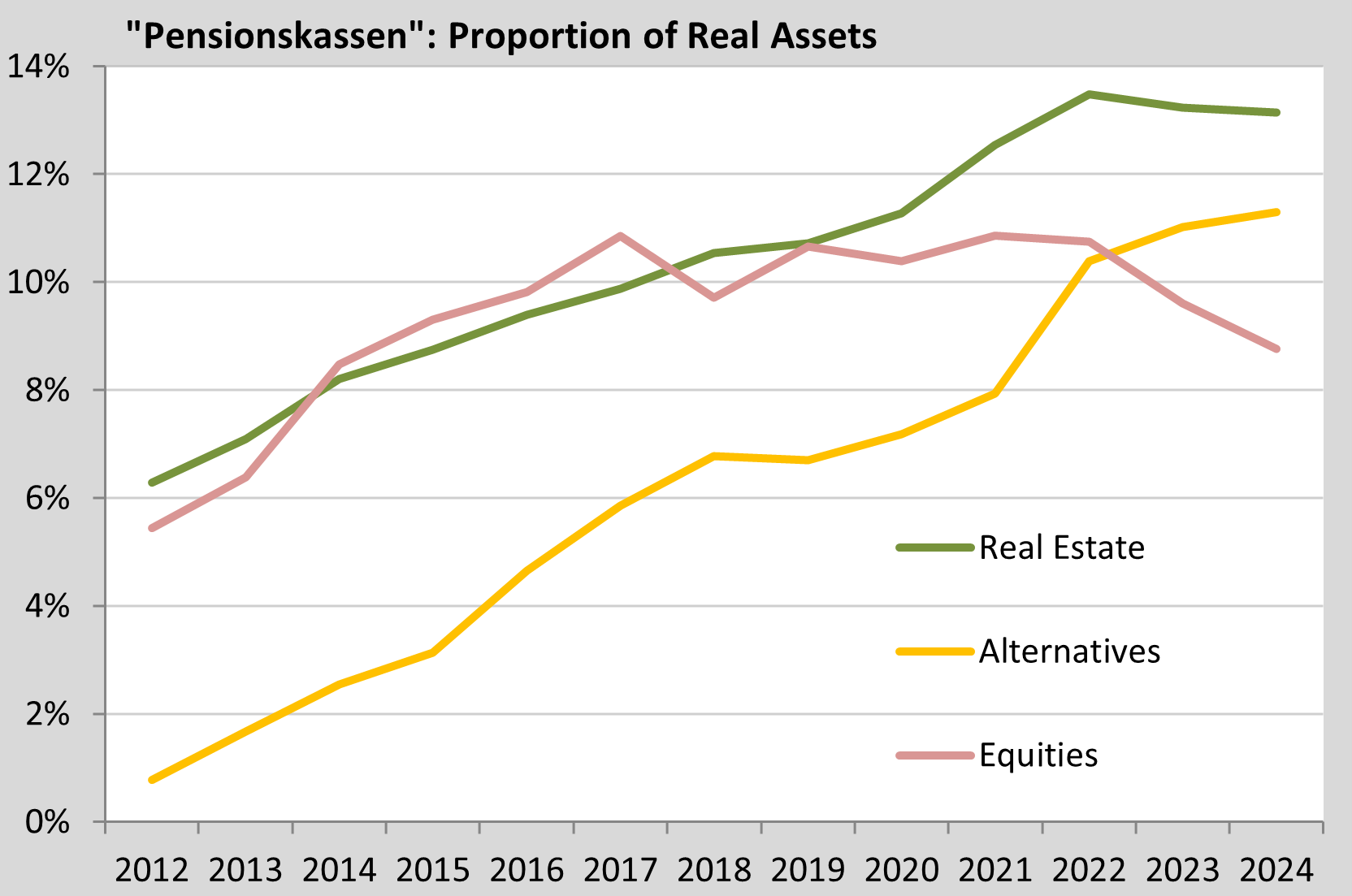
Capital Volume of "Pensionskassen" grew by five to around €212 billion in 2024. In company pension funds, the share of equities, real estate and alternatives in the total allocation has more than doubled since 2012 to around one third. However, equity exposure fell below 9% in 2024 for the second year in a row, and the weighting of real estate (13%) also declined slightly. Alternatives continued to grow to over 11%. In 2024, "Pensionskassen" achieved a net interest rate of almost 3% and a market value return of almost 4%, with company pension funds performing significantly better than the pension funds offered by insurance companies.
June 2025 - Asset Allocation Life Insurance: Equities decline, property stagnates, alternatives grow
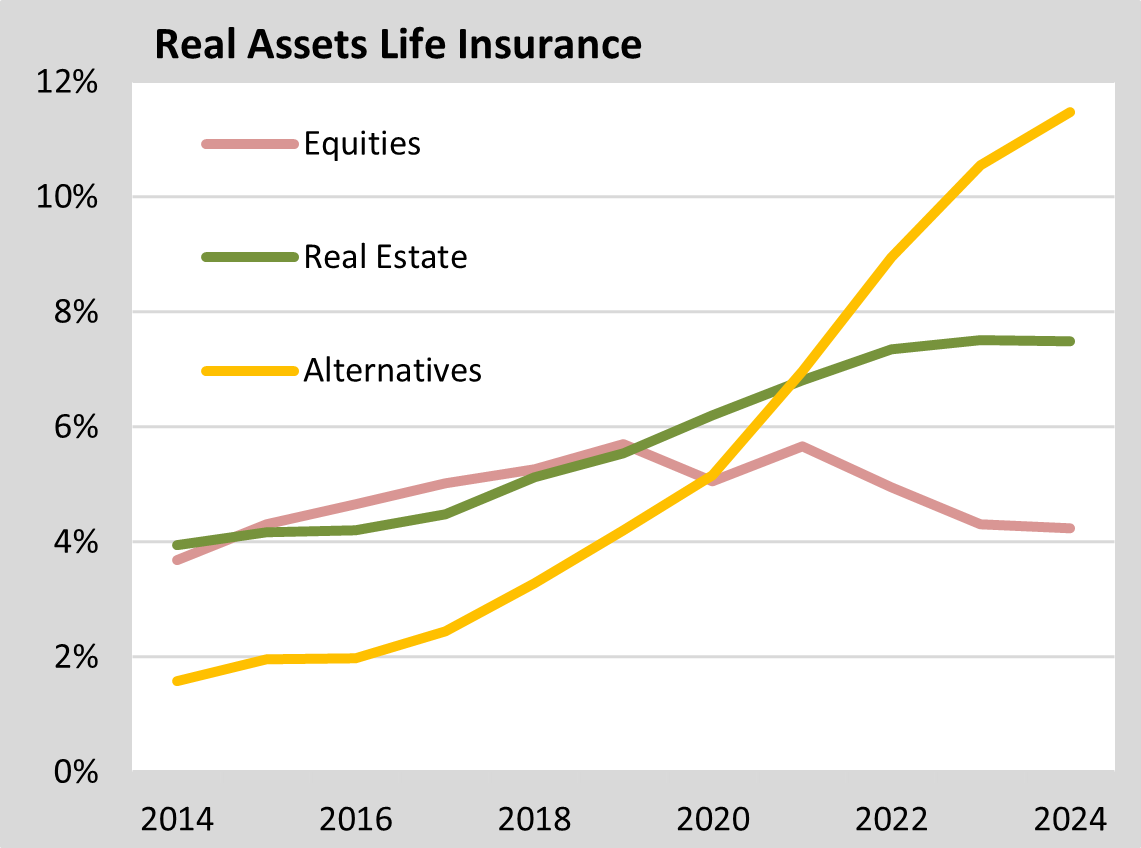
While the capital volume of traditional life insurance policies shrank by more than six billion euros in 2024, unit-linked policies increased by more than 35 billion euros to a new high of almost 216 billion euros. Market values are still around -7.5% below book values. The median net return in 2024 was 2.1% and the market value return was 2.6%. 40% of new investments totalling well over EUR 100 billion flowed into direct bonds, although the ratio fell slightly to just under 39%. Together with mortgage loans and bond funds, interest-bearing investments accounted for a good 75% of total investments at the end of 2024. The equity quota has fallen slightly further to just over 4%, the property quota remains at around 7.5% and the weighting of alternatives continues to grow to around 11.5%.
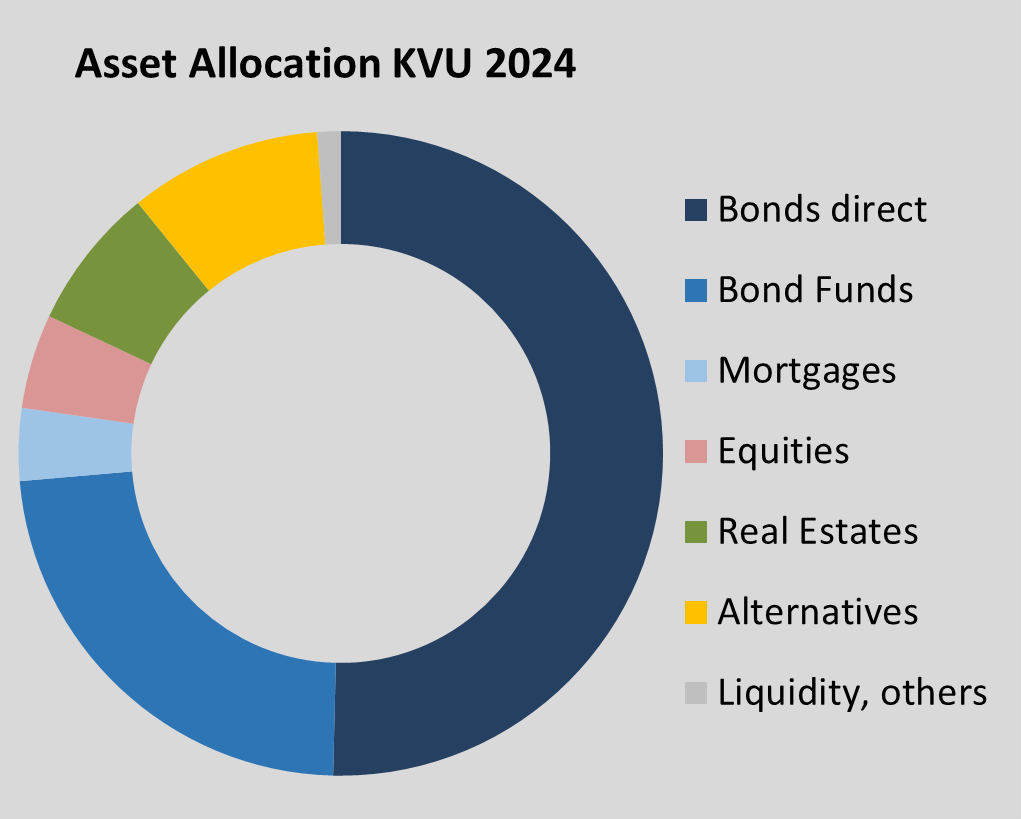
The investment volume of the 44 health insurance companies in Germany grew by 4% to 373 billion euros in 2024. The companies thus achieved a net return of around 2.3% and a market value return of around 4%. A good 40% of the new investments of more than EUR 40 billion made in 2024 flowed into direct bonds, which cover a good half of total investments. Together with mortgage loans and bond funds, interest-bearing investments have a total weighting of more than 77%. The share of equities has fallen further below five per cent. Real estate and alternatives (Private Equity, Private Debt, Infrastructure) account for a good 7% and almost 10% respectively.
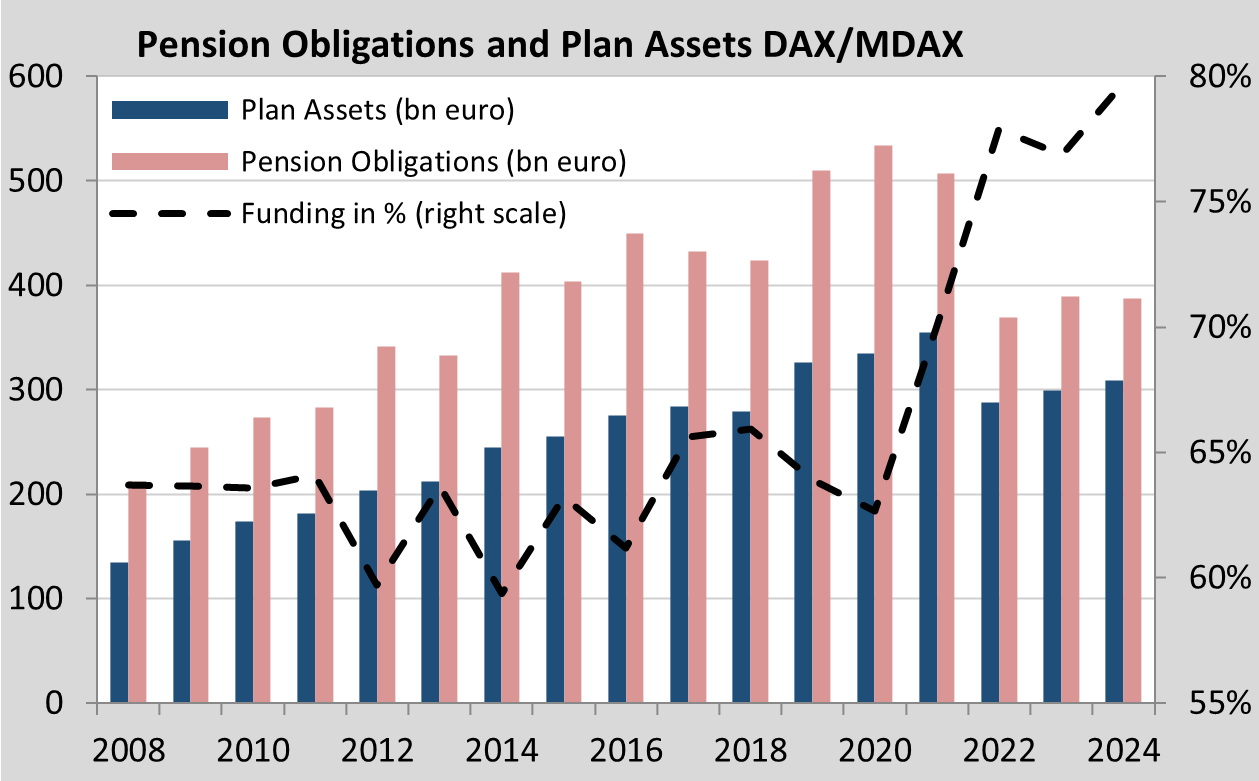
While the pension obligations fell by 0.5% in 2024 at an almost constant discount rate, plan assets increased by ten billion euros to 309 billion euros. The coverage ratio thus reached a new high of around 80%. Almost half of the capital is invested in bonds. The equity ratio has remained relatively constant overall at around 21%, although there were companies with both increasing and decreasing equity exposure. Real estate accounts for a good 6% of investments, while alternatives increased slightly to just under 8%. The remainder is invested in insurance contracts, derivatives and liquidity. The 38 DAX/MDAX companies with a minimum investment volume of EUR 500 million achieved a return of just over 5% in 2024 (capital-weighted value 5.1%, equally weighted mean 5.4%, median 4.8%). The results ranged from -1.3% to +14.7%.
